Learn About Top 10 Sexually Transmitted Infections Or STI

Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are often shrouded in stigma and misinformation. However, understanding these infections is crucial for maintaining sexual health and preventing their spread. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore ten common STIs, shedding light on what they are, their treatments, and crucial steps to avoid them.
1. Chlamydia
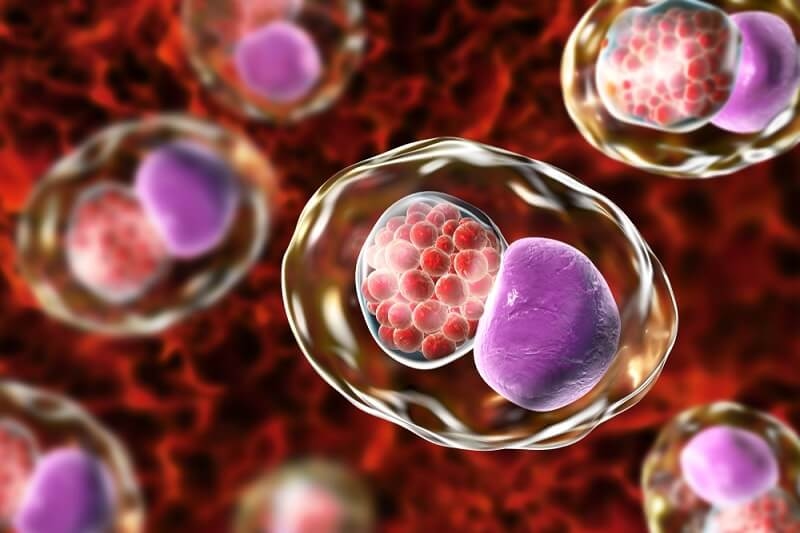
Chlamydia, caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, is the most commonly reported STI in the United States. It often presents no symptoms, leading to its being called "the silent infection." The symptoms that do occur include painful urination, abnormal vaginal or penile discharge, and lower abdominal pain. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to more severe complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and infertility in both genders. The condition is treatable with antibiotics like azithromycin or doxycycline. You must use condoms consistently during sexual activity and get tested regularly if you're sexually active to avoid infections. You must also talk to your sexual partners if you've been diagnosed with chlamydia so they can get tested and treated.
2. Crabs (Pubic Lice)
Pubic lice, commonly known as "crabs," are parasitic insects that infest the coarse hair of the genital area. They cause intense itching and discomfort. In some cases, small red or blue spots may appear at the site of the bites. Pubic lice can also infest coarse body hair like the chest or armpit. Special creams or shampoos are available for killing the lice and their eggs. You should thoroughly wash and disinfect clothing, bedding, and towels that have come into contact with an infected person. To avoid pubic lice, practice good personal hygiene, avoid sharing personal accessories, and avoid close contact with an infected person or their belongings.
3. Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which comes in HSV-1 (oral herpes) and HSV-2 (genital herpes). The condition is presented as painful sores or blisters in the genital or anal area. These sores can break open, ooze, and then form crusts. Antiviral medications like acyclovir can help manage symptoms, but there is no cure for herpes. To avoid genital herpes, practice safe sex by using condoms consistently and dental dams for oral sex. Open and honest communication about your sexual history with potential partners is also crucial.
4. Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It can be transmitted through sexual contact, sharing needles, or from mother to child during childbirth. The condition can also lead to chronic liver disease or liver cancer. While there is no cure, antiviral medications like tenofovir or entecavir can help manage the infection, reducing the risk of liver damage. To avoid hepatitis B, consider getting vaccinated, practice safe sex, and avoid sharing needles or personal items that may be contaminated.
5. Trichomoniasis
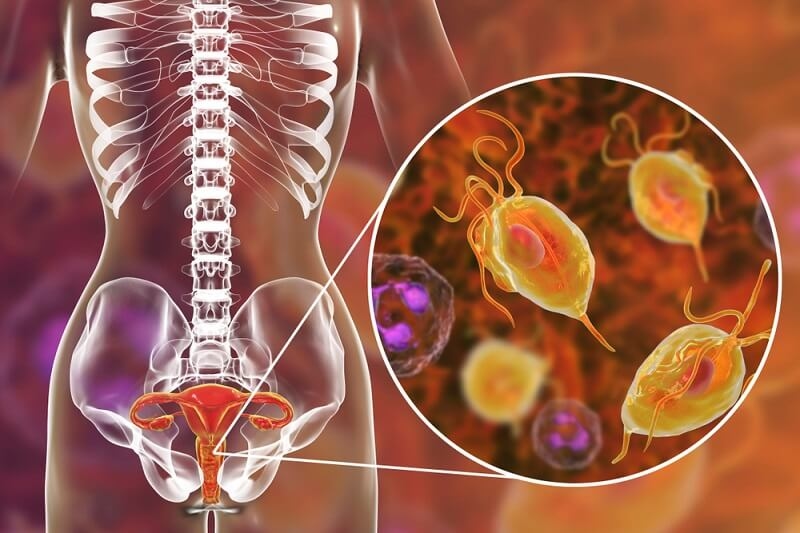
Trichomoniasis, caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, can result in itching, burning, and a frothy greenish-yellow discharge in women and urethral discomfort in men. This STI can affect both genders. Treatment involves a course of antibiotics like metronidazole or tinidazole. To avoid trichomoniasis, practice safe sex by using condoms consistently and get tested regularly, especially if you have multiple sexual partners.
6. HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a serious viral infection that attacks the immune system, potentially leading to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). It's transmitted through contact with certain body fluids, primarily during unprotected sexual intercourse and sharing needles for drug use. There is no cure for HIV, but antiretroviral therapy (ART) can control the virus's progression, allowing individuals to lead relatively healthy lives. To avoid HIV, use condoms consistently, get tested regularly, and consider pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) if you are at higher risk, such as having a partner with HIV.
7. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
-1693823151-r.jpg)
HPV is an incredibly common viral infection, with over 100 different strains. Some strains can lead to genital warts and cervical, anal, and throat cancers. Vaccination is available for prevention and is highly effective when administered before exposure to the virus. While the virus is not cured, treatments can manage symptoms like genital warts. To avoid HPV, vaccinate, practice safe sex, and discuss your vaccination and sexual history with potential partners.
8. Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes painless, raised bumps on the skin's surface. These bumps can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found in the genital area in adults. It can be spread through close skin-to-skin contact and by sharing personal items. While the condition often clears on its own, it can be treated by a healthcare professional if necessary. To avoid it, avoid close contact with infected individuals and their belongings, and practice good hygiene.
9. Syphilis
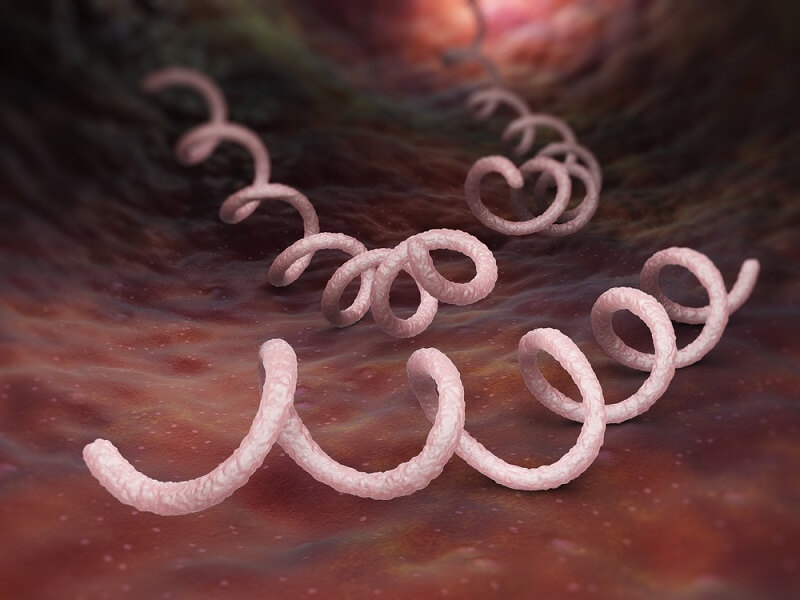
Syphilis is a bacterial STI caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum. It progresses through stages, each with distinct symptoms. Symptoms can range from sores or ulcers in the genital, mouth, or rectal areas to rashes and fever. If untreated, syphilis can lead to severe complications, affecting various organs and tissues, including the heart and brain. However, it's treatable with antibiotics, typically penicillin. Early detection and treatment are crucial. To avoid syphilis, practice safe sex by using condoms consistently and get tested regularly.
10. Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is another bacterial STI caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It can lead to severe complications if left untreated, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and infertility in both sexes. Symptoms can include painful urination, abnormal discharge, and discomfort. Like chlamydia, it can also be asymptomatic. It's treatable with antibiotics, but the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains is a growing concern. To avoid gonorrhea, practice safe sex, use condoms consistently, and get tested regularly, especially if you have multiple sexual partners.
Conclusion
Sexually transmitted infections are a significant public health concern, but knowledge is a powerful tool in preventing and managing them. Regular testing, open communication with partners, practicing safe sex, and getting vaccinated when possible are all essential steps in safeguarding your sexual well-being. Remember, seeking medical advice and treatment promptly can make a significant difference in managing and preventing the complications of these infections. Your sexual health is a priority, and by staying informed, you can protect yourself and your partners.
This content was created by AI
-1717753922-r.jpg)