Understanding Everything About The Bee Sting Allergies

Nature has given us the beautiful gift of creation, and every part of it proves the unique existence of life. Every organism plays a distinct role in keeping the balance of life. Among these organisms, the bee is an insect known for pollination and the growth of plants. Although a beautiful creation of nature, bees are instinctively protective of themselves and are designed to attack their threats. Their defense mechanism is barbed, which stings and releases toxins to numb the enemy.
We, humans, pose a natural threat to the bees, given our body size and strength. Although, our bodies are not entirely acquired to the bee stings and can cause an allergic reaction. This reaction can lead to severe health complications if not promptly addressed. Lets understand what you must know about bee sting allergies and the appropriate treatments.
What to Know About Bee Sting Allergies:
You can define bee sting allergies as a reaction given by our body when the barb of the bee comes into contact with our skin. During this process, venom is injected into our body, which triggers this reaction. While most people experience only mild pain, swelling, and redness at the sting site, others may develop a dangerous allergic response. This condition arises when the immune system overreacts to specific proteins in the bee venom, producing an exaggerated immune response.
How Common Are Bee Sting Allergies?
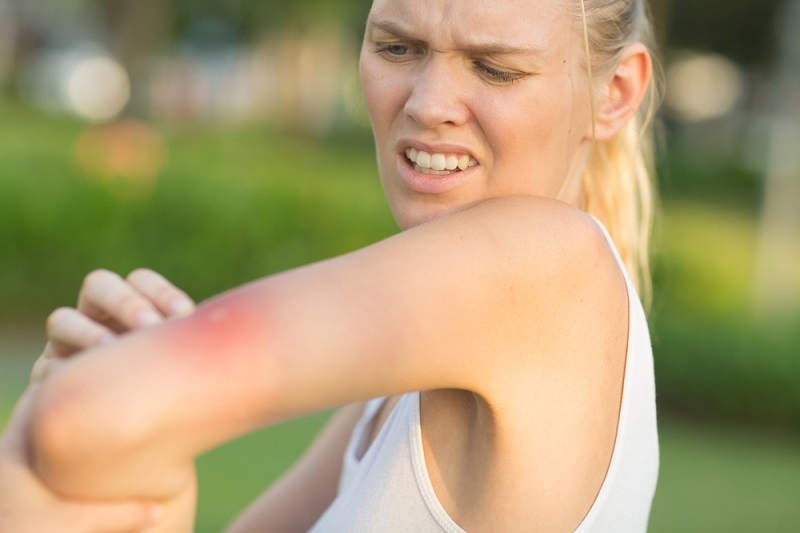

The chances of you getting bee sting allergies are uncommon, given they only affect 5% of the population. Although, it is vital to know the difference between an ordinary bee sting and bee sting allergies. The regular symptoms of a bee sting include pain, itching, swelling, and redness around the sting site. However, bee sting allergies may experience a systemic response involving various body systems and require immediate medical attention.
Causes of the Allergic Reaction:
The cause of bee sting allergies is a bee venom that contains several allergenic components, such as phospholipase and hyaluronidase. These components cause the immune system to respond aggressively. If you have bee sting allergies, your immune system identifies these components as harmful invaders, even though they might be harmless to others.
Symptoms of Bee Sting Allergies:
Even though it is a medical professionals job to identify the difference between a regular bee sting and bee sting allergies, you must know the basics. The symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may manifest within minutes or hours after the sting. Some common symptoms include:
Localized Reactions:
Pain and Swelling at the Sting Site:
When stung by a bee, the primary reaction is swelling of the affected area and pain. The pain can be sharp when the area is touched, and the swelling is the body's reaction to fight the venom. The affected area may become red and tender to the touch, indicating an inflammatory response.
b) Redness and Warmth:
The sting site may become red, and the surrounding skin may feel warm. This signifies inflammation as the body's immune system tries to neutralize the venom and repair the damaged tissue.
Itching and Hives around the Sting Area:
In addition to the visible symptoms, you might feel itching and notice hives around the affected area. It is not recommended to scratch the itchy surface as it might increase inflammation or, worse, an allergic reaction.
Systemic Reactions:
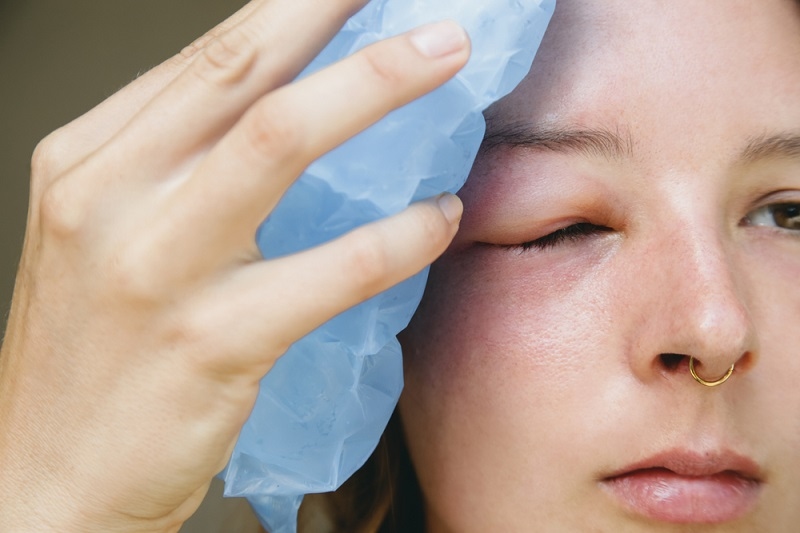
Severe Swelling of the Face, Throat, or Tongue:
Contrary to the regular reactions, bee sting allergies also cause swelling in other body parts. This could involve swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, making it challenging to handle. When these areas swell, it can cause difficulty breathing and swallowing, quickly becoming life-threatening.
Difficulty Breathing or Shortness of Breath:
When your body isn't suiting the alien component entering it, a series of functional responses can be noticed. Bee sting allergies can also affect the respiratory tract, causing shortness of breath. This is a result of the swelling in the esophagus that creates difficulty in breathing, swallowing food, or even wheezing.
Nausea, Vomiting, or Diarrhea:
Bee sting allergies can trigger gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. These symptoms may arise due to the overall stress on the body caused by the allergic reaction. As an involuntary response to bee sting allergies, your body also tends to lower your blood pressure. This might result in you feeling lightheaded or dizzy. In some cases, individuals may even faint due to insufficient blood flow to the brain.
Rapid Heartbeat or Palpitations:
Bee sting allergies might also affect the heart rate when the body considers it a trauma. This could result in your chest feeling heavy and/or rapid heart beating. These symptoms may exacerbate feelings of anxiety and discomfort during an allergic episode.
Loss of Consciousness or Anaphylaxis (a life-threatening reaction):
The extremities of bee sting allergies cause anaphylaxis, which could be life-threatening. In this type of reaction, there is a sudden drop in blood pressure, loss of consciousness, and even cardiac arrest. I would suggest immediate medical attention and consulting professionals at this stage.
5) Treatment for Bee Sting Reactions:
The immediate first step to a bee sting is to detect the affected area and remove the barb or the stinger from the body. It is suggested not to use a pair of tweezers to avoid more venom in the body. Once removed, clean the affected area with soap and water to neutralize the reaction as much as possible. You can apply a cold compress to reduce pain and swelling. For localized reactions, over-the-counter pain relievers and antihistamines can help alleviate discomfort and itching. Topical corticosteroids may also be beneficial in reducing inflammation.
Although bee sting allergies can be fatal, you must seek medical attention if you are experiencing allergic reactions. In case of anaphylaxis, it is essential to administer epinephrine in the body. An auto-injector like Epipen can do this. If experiencing anaphylaxis, even after using an epinephrine auto-injector, seeking emergency medical attention remains crucial to prevent further complications.
Conclusion:
Bee sting allergies can be a severe health concern if not focused on the symptoms in time. While these allergies are not widespread, it is crucial to recognize the difference between standard and allergic reactions to bee stings. If you or someone you know has a known bee sting allergy, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector and seeking immediate medical attention after a sting can prevent life-threatening complications. Bees are essential for our ecosystem, and we can stay safe with proper awareness and precaution.
This content was created by AI
-1717753922-r.jpg)