What is Asthma? Types, Causes, Symptoms and Treatments

Breathing is a fundamental process that sustains our existence and overall well-being. It ensures our organs receive the vital oxygen they require to function optimally. However, various factors can disrupt this essential function, leading to different respiratory conditions. One of the most prevalent among these conditions is asthma, which is both familiar and treatable.
Asthma can be defined as a chronic lung disease caused by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. While it is typically manageable, it can turn life-threatening if not addressed promptly. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of asthma, its types, symptoms, triggers, and effective management strategies.
Types of Asthma
Asthma comes in various forms, each with its unique symptoms. Understanding these types is crucial for effective management. The main types of asthma include:
- Allergic Asthma: This type of asthma is triggered by allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Exposure to these allergens can lead to asthma symptoms.
- Exercise-Induced Asthma (EIA): Physical activity can provoke EIA in some individuals. Symptoms typically occur during or after exercise and may include coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Occupational Asthma: Certain workplace irritants or allergens can lead to occupational asthma. People working in environments exposed to dust, chemicals, or fumes are at risk.
- Non-Allergic Asthma: Unlike allergic asthma, non-allergic asthma is not triggered by allergens. Instead, it can be provoked by factors such as cold air, respiratory infections, or even stress.
- Childhood Asthma: Asthma can develop in childhood and persist into adulthood. Identifying and managing asthma early in life is essential for long-term health.
Common Signs and Symptoms
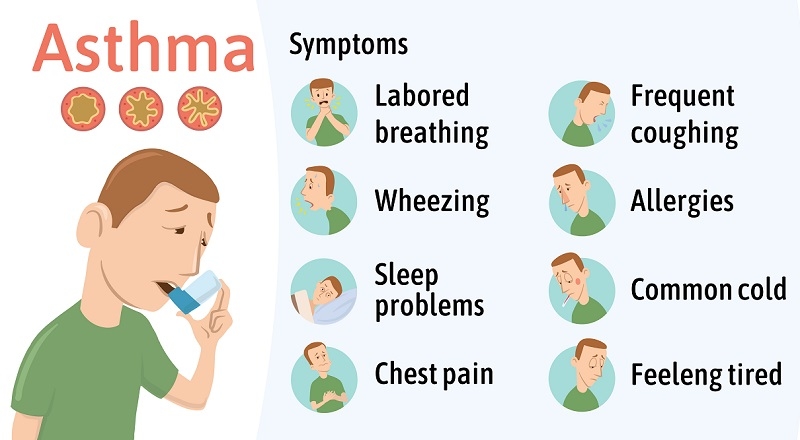
Asthma manifests through various signs and symptoms, which may vary in intensity. It is vital to recognize these indicators to seek timely medical intervention. Some common asthma signs and symptoms include:
- Shortness of Breath: Individuals with asthma often experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or at night.
- Wheezing: Wheezing is a characteristic high-pitched whistling sound that occurs when breathing, particularly during exhalation.
- Coughing: Persistent coughing, especially at night or early in the morning, can indicate asthma.
- Chest Tightness: A sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest is a common symptom, often described as feeling like a band around the chest.
- Coughing or Wheezing in Children: Children with asthma may exhibit symptoms such as frequent coughing, wheezing, or recurrent respiratory infections.
Asthma Triggers

Understanding what can trigger asthma symptoms is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Common asthma triggers include:
- Allergens: Substances like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold can set off asthma symptoms in allergic individuals.
- Exercise: Vigorous physical activity can induce asthma symptoms, especially in cold or dry air.
- Cold Air: Exposure to cold air can cause airway constriction and trigger asthma symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate asthma symptoms in some individuals.
- Respiratory Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections can worsen asthma symptoms, making it essential to manage these conditions effectively.
Asthma Management
Asthma management varies based on its severity and individual factors. For milder cases, lifestyle modifications can be effective. These include:
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers, such as allergens or strenuous exercise in cold air, is essential.
- Regular Exercise: Regular, moderate exercise can help strengthen the lungs and improve asthma control.
- Stress Reduction: Managing stress through meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can prevent stress-induced asthma symptoms.
In more severe cases, medical intervention is necessary. Medications like inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and leukotriene modifiers can help control inflammation and symptoms. Oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe asthma attacks.
Preventing Asthma
Preventing asthma involves adopting a proactive approach to managing your health. Some preventive measures include:
- Avoiding Allergens: Minimize exposure to allergens by keeping your living space clean and well-ventilated.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can boost lung function and overall well-being.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in nutrients can support your immune system and respiratory health.
- Adequate Rest: Getting enough sleep is crucial for overall health and can help reduce stress.
Asthma and Exercise
The relationship between asthma and stress is complex. Stress is a common trigger for asthma symptoms and can exacerbate the condition in individuals who already have it. When under stress, the body's natural response is to release stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can cause the airways to constrict, making it harder to breathe, especially for those with asthma. Managing stress is an essential aspect of asthma management. Here are some stress-reduction strategies that can help individuals with asthma:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness techniques, including meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals manage stress and anxiety. These practices promote relaxation and can improve overall well-being.
- Yoga: This combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to reduce stress and improve lung function. It can be an excellent addition to an asthma management plan.
- Regular Exercise: Regular, moderate-intensity exercise can reduce stress and improve mood. It can also strengthen the respiratory muscles, benefiting individuals with asthma.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough restorative sleep is crucial for stress management. Poor sleep can lead to increased stress levels, so it's essential to establish healthy sleep habits.
- Seeking Support: Talking to a therapist or counselor can provide valuable tools for managing stress. Support from friends and family can also be instrumental in reducing stress levels.
Asthma and Allergies

Allergies and asthma often go hand in hand. Allergic asthma is a specific type triggered by allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. These allergens can cause inflammation in the airways, leading to asthma symptoms. Identifying and managing allergies is a vital component of asthma care. Here are some steps you can take to address allergies that may be contributing to your asthma:
- Allergy Testing: Consult with an allergist for allergy testing. This can help pinpoint specific allergens that trigger your asthma symptoms.
- Allergen Avoidance: Once you know your allergy triggers, take steps to avoid them. This may include using air purifiers, keeping your home clean and free from dust mites, and reducing exposure to pollen during high seasons.
- Allergy Medications: Allergy medications, such as antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids, can help manage allergic reactions and reduce asthma symptoms.
- Immunotherapy: In some cases, allergen immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be recommended to desensitize your immune system to specific allergens over time.
- Environmental Control: Make modifications to your environment to reduce allergen exposure. For example, consider using allergen-proof covers on pillows and mattresses, and keep pets out of bedrooms if you are allergic to animal dander.
Conclusion
If you suspect you have asthma or experience any symptoms, seek medical evaluation and treatment. Timely diagnosis and management are crucial for ensuring a high quality of life for individuals with asthma. Remember that asthma can be effectively controlled with the right approach, allowing you to lead a healthy and active life.
This content was created by AI
-1717753922-r.jpg)